

The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of CHRPE lesions in FAP and those at risk were calculated. Data were analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Science version 17.0 (SPSS 17.0, Chicago, Illinois, USA). If they were found to have polyps in the colon, an upper gastro intestinal endoscopy was also performed to look for polyps in the stomach and duodenum which may have malignant potential. Those who had ophthalmological screening for CHRPE lesions underwent a flexible sigmoidoscopy to look for the presence of polyps in the colon. A common side effect of this procedure was transient blurring of vision, which reversed in a few hours. If found, the site, size, number and shape of lesions were documented.
After the pupils were fully dilated, slit lamp and indirect ophthalmoscopic examinations were performed to identify CHRPE lesions. In all individuals, the eyes were checked for visual acuity as screening, followed by dilatation of the pupils using tropicamide and phenylephrine ophthalmic solution. Ophthalmological examination was performed by an experienced ophthalmologist at North Colombo Teaching Hospital, Ragama. Those who consented were subjected to ophthalmological screening. A consent form was prepared in three languages (Sinhala, English and Tamil) and informed written consent was taken from all individuals participating in the activities of the registry.
Bear tracks retina registration#
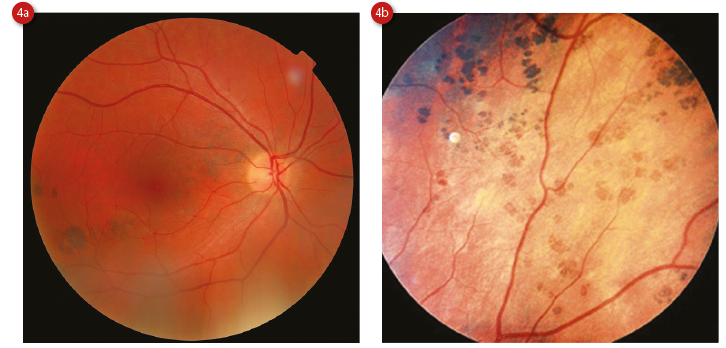
All FAP patients and individuals at risk were invited for registration in the FAP registry. The proforma contained all details about the patient including a plan of follow up. Proformas were prepared for FAP patients and relatives at risk. The aim of our study was to assess the value of ophthalmic screening, to find the association of CHRPE lesions in individuals with FAP or their family members in a local population and to describe the pattern of distribution of CHRPE lesions in these individuals in order to assess the feasibility of using it as a low cost, non invasive screening test to detect FAP.Īll individuals with a diagnosis of familial adenomatous polyposis made at the professorial surgical unit, Ragama between 19, were traced using clinical notes, endoscopic registers and admission books. The prevelance of CHRPE in the normal population is between 1.2% to 4.4% which increases its specificity for screening. Oval CHRPE lesions with fishtail shaped hypo-pigmented change at one or both ends may be associated with FAP. Lesions may be oval, round or bean shaped. The size of a CHRPE lesion is variable but most are similar in diameter to the optic disc. It may be single or multiple, unilateral or bilateral. It is a darkly pigmented lesion with a depigmented halo in the retina. It is the most common and earliest extra colonic manifestation amongst FAP populations which may be present at birth (80%) or shortly after birth. This makes detection of CHRPE in asymptomatic individuals who are at risk an attractive screening option. The global prevalence of CHRPE in individuals with the APC mutation is ninety percent. It is commonly caused by a truncating mutation in the codons between 4 of the APC gene. CHRPE was first described by Blair and Trempe in 1980. For example, mutations in codon 1597 are known to be associated with desmoid tumours and absent CHRPE.

FAP related CHRPE may not be seen in all with the FAP genotype. Disease has a hundred percent penetrance when the genotype is present. The condition is autosomal dominant making half of the off spring of an affected individual parent at risk of developing FAP. Familial adenomatous polyposis is caused by mutations in the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene, a tumour suppressor gene, located in the long arm of chromosome 5. FAP is also associated with the presence of polyps in the upper gastro intestinal tract in 90 to 100 percent. Patients may develop extra intestinal manifestations such as congenital hypertrophy of retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE), sebaceous cysts (51%), desmoids tumours (26%), and in lesser proportions, osteomas, lipomas (Gardner’s syndrome ) and extra intestinal malignancies hepatomas, retinoblastomas and brain tumours (Turcot’s syndrome). Therefore early diagnosis and appropriate treatment is essential. If left, these polyps will invariably transform, through the adenoma-carcinoma sequence, to colorectal malignancy. Patients develop multiple adenomatous polyps in the colon varying from a hundred to thousands in number. Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is a genetic disorder transmitted in an autosomal dominant pattern.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
